Embracing the Future: Integrating Generative AI in Recruitment
By leveraging generative AI in recruitment, organizations can improve candidate engagement, gain valuable talent acquisition analytics, transform the interviewing process and enhance job postings. While promising, leaders should be cautious and consider the challenges before adopting the technology. AGS is pleased to share this article from guest blogger Everest Group Practice Director Sailesh Hota.
As technology advances at an unprecedented pace, enterprises across the globe are entering a new era of innovation, efficiency, and forward-thinking strategies. In the past few months, generative AI has emerged as a game-changer in many sectors with far-reaching implications.
Machine learning models have unlocked the ability in AI tools to mimic human-like responses by understanding text and generating responses. Generative AI spans multiple areas beyond text generation and extends into content generation in other formats.
The capability to engage in natural conversations and produce coherent content presents potential for large-scale transformation and disruption in various sectors, including HR and recruitment. Let’s explore its potential further.
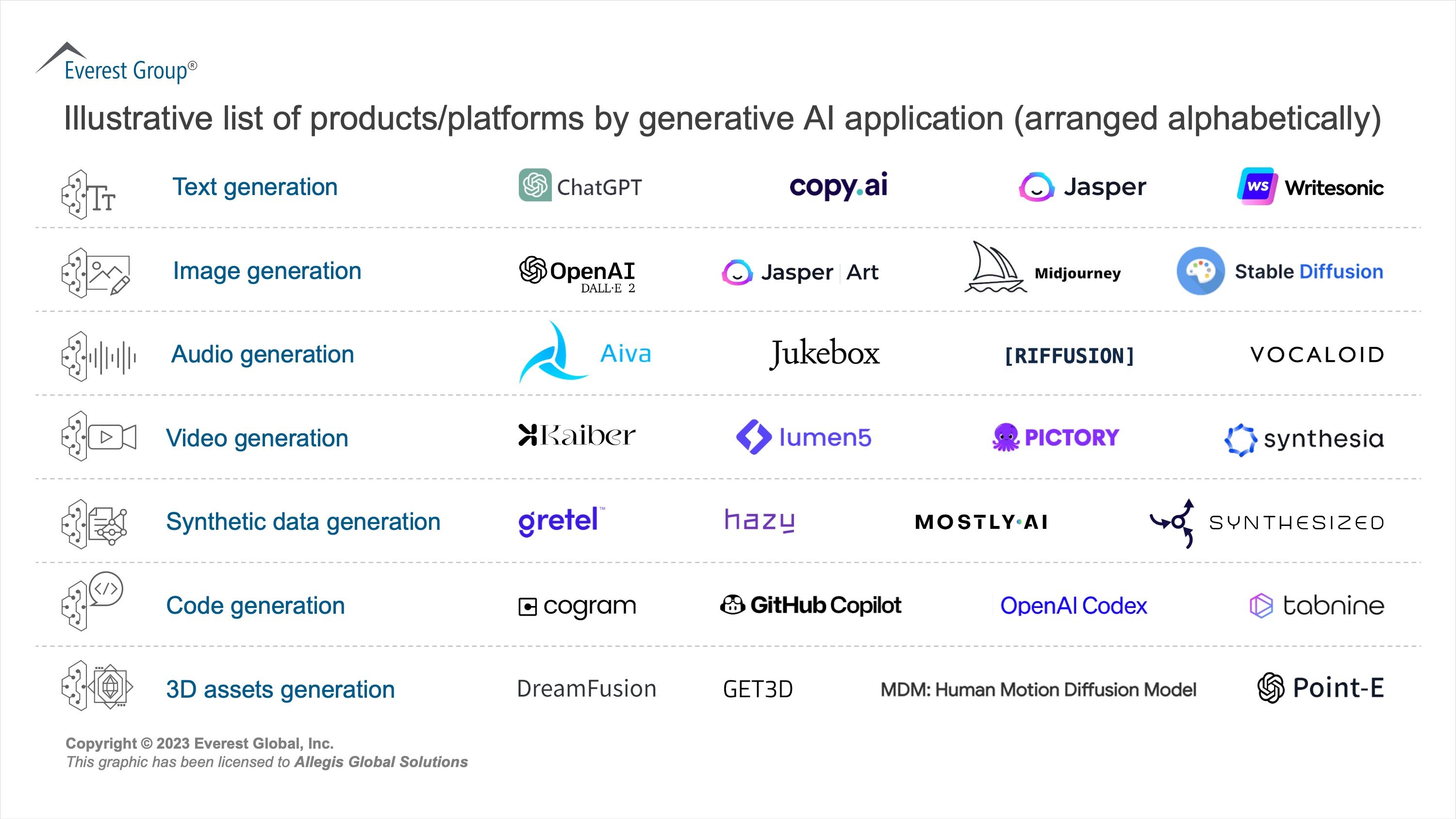
Exploring the Potential Benefits of Generative AI in Recruitment
Embracing generative AI offers businesses a transformative approach to talent acquisition, streamlining and optimizing the recruitment process while delivering exceptional results. Enterprises can tap into a vast array of applications, including content creation, language translation, and candidate management – all of which can enhance recruiters’ productivity, allowing them to focus on strategic aspects of recruitment instead of depleting time and energy on administrative and transactional tasks.
Some of the prominent use cases are as follows:
Improving Candidate Engagement
Candidate relationship management (CRM) platforms and recruitment marketing tools have started to become more commonplace as all enterprises race to the top of the “employer brand” mountain. This has created a need for regular engagement with top candidate pools via drip campaigns, email blasts, and social media initiatives. Generative AI can play a pivotal role on this front.
A few examples include AI-driven point solutions that can be used to engage with candidates and answer their queries over email as well as utilizing generative AI to create tailored campaigns that add personalization for high-value talent pools.
Providing Deep Analytics for Talent Acquisition
Macroeconomic and talent landscape volatility over the past half-decade has sparked a demand for effective analytics and market intelligence. This has given rise to new complexities in terms of data representation and analysis. The continuous variance in market conditions has made analyzing patterns and identifying trends difficult in recent times.
Generative AI models could play a significant role in addressing this problem through their ability to analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured data. These models can identify patterns and market trends and generate comprehensive analysis in the formats of dashboards, charts, and data cuts. Generative AI-based tools can help leaders and hiring managers create custom analyses more quickly with a simple prompt.
Transforming the Assessment and Interview Process
The interview phase is vital for evaluating a candidate’s suitability for an organization. Using generative AI can greatly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of interviews, allowing recruiters to better understand a candidate’s abilities. Here are some examples offering promise:
- AI-powered chatbots can simulate real interview situations and generate candidate responses, providing valuable insights into their performance
- Generative AI’s heightened natural language processing capabilities could significantly improve the efficacy of resume parsing and CV analysis
By using these technologies, businesses can streamline initial screening, quickly identifying any concerns or outstanding qualities in candidates. Furthermore, generative AI-integrated chatbots would make it easier to give candidates constructive feedback from the offset, creating a positive and transparent recruitment experience for everyone involved.
Enhancing Job Descriptions and Talent Profiles
Generative AI can also assist in creating compelling and inclusive job descriptions that reflect the company’s ethos and values while also appealing to a wider target audience. By analyzing vast amounts of data, generative AI can learn from existing job postings and company-specific language, generating unique and engaging descriptions that resonate with potential candidates.
Moreover, generative AI also can help draft ideal candidate profiles by analyzing and extracting profile information of top performers. By understanding the correlation between skill sets and performance, enterprises can make data-driven decisions to identify and match suitable candidates for specific roles.
Will Generative AI Replace Talent Acquisition Professionals?
While the shock factor of this question is high, the possibility of AI replacing human intervention in recruitment is still low.
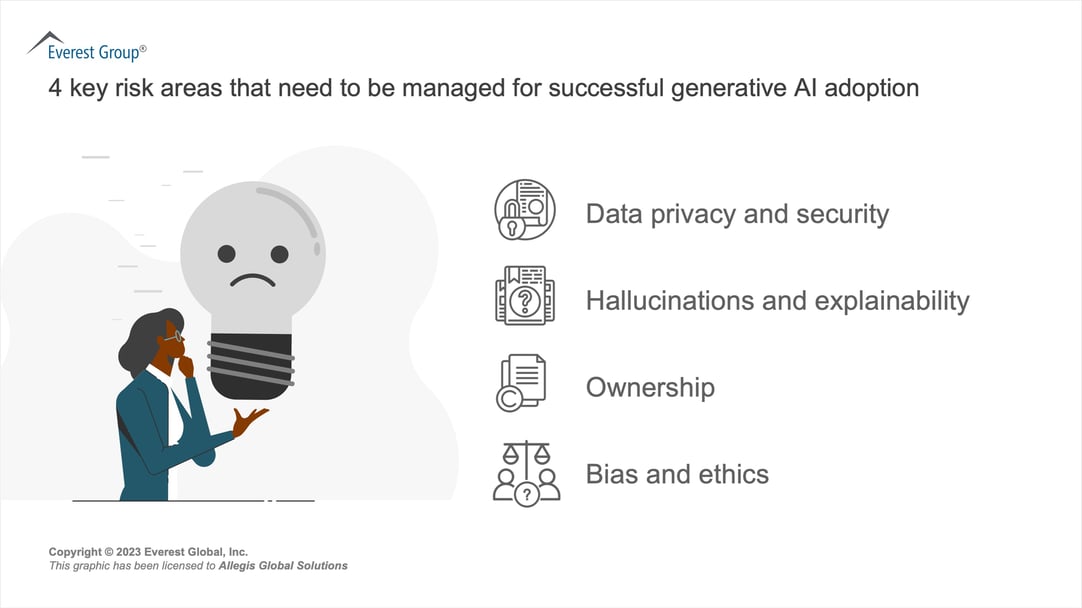
While the technology holds tremendous promise, the following concerns have surfaced about the use of generative AI in recruitment:
- Data privacy and security: Democratizing usage magnifies the avenues for potential information leakage such as employees sharing personally identifiable information (PII) in prompts and regulatory fallout from data collection and retention without proper disclosure. Organizational data also stands at risk of breach when used to fine-tune generative AI models.
- Hallucinations and explainability: Hallucinations refer to the generation of outputs that may appear plausible but are either factually incorrect or out of context. This can occur due to insufficient training data, inherent biases, or misunderstanding. The lack of any visibility in the reasoning process and the inability to trace outputs back to specific data points makes it difficult to explain the results generated by AI systems.
- Ownership: The absence of any relevant IP or copyright laws at the moment has created ambiguity around the legal ownership of content created by generative AI. This ambiguity can lead to situations where multiple parties claim ownership of generated content resulting in legal battles.
- Ethics and bias: Training generative AI systems on extensive datasets can perpetuate and amplify biases present in the data, resulting in biased outputs that reinforce stereotypes and discrimination.
Furthermore, organizations also need to address various sustainability concerns that call for an AI strategy that is aligned with the firm’s environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles.
Future Outlook for Generative AI in Recruitment
Organizations should remain cautiously optimistic when considering the wide-ranging possibilities associated with generative AI in many fields. While generative AI in recruitment and talent acquisition can offer many positive benefits, enterprise leaders should stay mindful of the evident pitfalls and potential risks before deeply integrating the technology within existing systems and processes.
-min.png)





